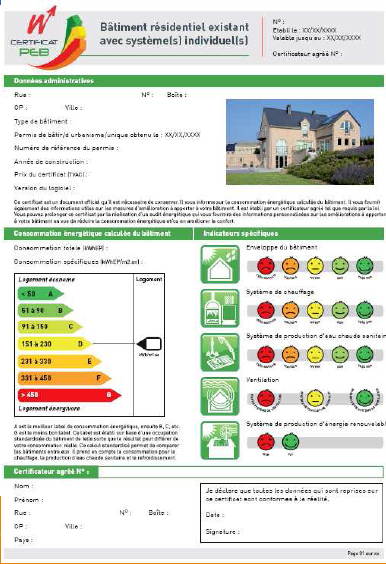
The energy certification is essential for assessing and improving the energy performance of a building. It provides clear and precise information on energy consumption, allowing owners and buyers to make informed choices. Since April 1, 2023, the most energy-intensive homes must undergo a mandatory energy audit before sale, thus ensuring a commitment to better energy efficiency and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
The energy certification is a crucial aspect for evaluating the energy performance of buildings. It comes in various diagnostics, certifications, and audits that contribute to better management of energy consumption and reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. Here is a glossary of key terms associated with this field.
Energy Performance Diagnosis (DPE): The DPE is essential for assessing the energy and climatic performance of a home or building. Rated from A (very efficient) to G (very energy-intensive), the DPE informs property owners and potential buyers about a property’s energy consumption and CO2 emissions.
Energy Audit: Since April 1, 2023, the most energy-intensive homes must undergo an energy audit in case of sale. This audit identifies the necessary work to improve the energy performance of the home and establish a renovation pathway.
RGE (Recognized Guarantee of the Environment) Certification: This certification certifies that craftsmen and companies meet objective criteria of competence and quality in the field of energy improvement of buildings. However, it is important to note that it does not necessarily guarantee the verification of the work done.
Energy Savings Certificates (CEE): The CEE are a mechanism encouraging actors in the energy market to achieve energy savings. They grant certificates based on the efforts made to reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, thereby motivating the transition to more sustainable practices.
Energy Class: It represents the classification of a building on a scale from A to G, according to its energy performance. A high energy class (A or B) means better energy efficiency and lower consumption, while a low class (F or G) indicates significant energy needs.
BREEAM Certification: Highly valued in sustainable construction projects, BREEAM certification assesses the environmental performance of buildings through specific criteria such as energy management, waste management, and materials. It contributes to promoting energy efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Energy Label: Affixed to real estate diagnostics, this label provides information about the energy consumption of the home. Labels A and B indicate energy-efficient homes, while labels F and G signal energy-guzzling ones.
Energy Performance: This indicator measures the efficiency of a building in terms of energy consumption. Good energy performance indicates reduced consumption and better management of energy resources.
Embodied Energy: This refers to the amount of energy required to produce and transport a material to its place of use. Considering embodied energy in certifications helps optimize the production and implementation chain of materials to reduce the ecological footprint.
Urban Regeneration: These are initiatives aimed at renovating and improving urban areas to make them more sustainable and energy-efficient. Urban regeneration involves numerous certifications and audits to ensure environmentally friendly constructions.
Renewable Energy: Integrating renewable energy sources in a building, such as solar panels or wind systems, enhances its energy certification by reducing dependence on fossil energy sources.

FAQ on Energy Certification
Q: What is energy certification?
A: The energy certification assesses the energy efficiency of a building, providing an energy rating from A (very efficient) to G (very inefficient).
Q: How is the energy class of an apartment calculated?
A: The energy class is calculated based on several criteria, such as annual energy consumption, type of heating, insulation, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Q: When must the energy certification be produced?
A: The energy certification must be produced when selling or renting out a property. It is also necessary to benefit from certain financial aids for energy renovation works.
Q: What are the advantages of energy certification for an owner?
A: The energy certification allows owners to identify possible improvements to reduce energy costs, increase the value of their property, and attract buyers or tenants concerned about ecological impact.
Q: How to obtain energy certification?
A: To obtain an energy certification, it is recommended to hire a certified diagnostician who will conduct a detailed evaluation of the property and issue the certificate accordingly.
Q: What is the difference between a DPE and an energy certification?
A: The Energy Performance Diagnosis (DPE) is the official report that informs about the energy and climatic performance of a building, while the energy certification is the overall process that includes evaluation and issuance of the certificate, including recommendations for improving energy performance.
Q: Who is responsible for conducting the energy audit necessary for certification?
A: The energy audit must be conducted by a certified professional, often a diagnostician or an engineer specialized in the energy performance of buildings.
Q: Is energy certification mandatory?
A: Yes, energy certification is mandatory in several contexts, including when selling or renting out properties, for new buildings, and for certain energy renovation processes requiring government subsidies.
Q: How long is an energy certification valid?
A: The energy certification is generally valid for a period of ten years, unless major renovation works have been carried out in the meantime.
Articles similaires
Thank you!
We will contact you soon.