Revolutionary discovery of the early 19th century, the photovoltaic effect, highlighted by Edmond Becquerel in 1839, paves the way for an era of renewable energies. Thanks to this phenomenon, certain materials, known as semiconductors, transform sunlight into electricity, without any destruction or consumption of matter. This mechanism allows for a direct conversion of light energy into electric current, thus marking a significant advancement in the field of solar technologies. Photovoltaic cells, true marvels of technology, are essential in the current energy transition, providing a sustainable and ecological alternative to conventional energy.
Glossary: Everything You Need to Know About the Photovoltaic Effect
The photovoltaic effect is a fascinating phenomenon that allows for the production of electricity from solar radiation. Highlighted in 1839 by scientist Edmond Becquerel, this effect relies on the properties of certain materials called semiconductors. When exposed to light, these materials generate electricity through the transfer of energy between photons and electrons. This effect is the foundation of the solar technologies we use today.
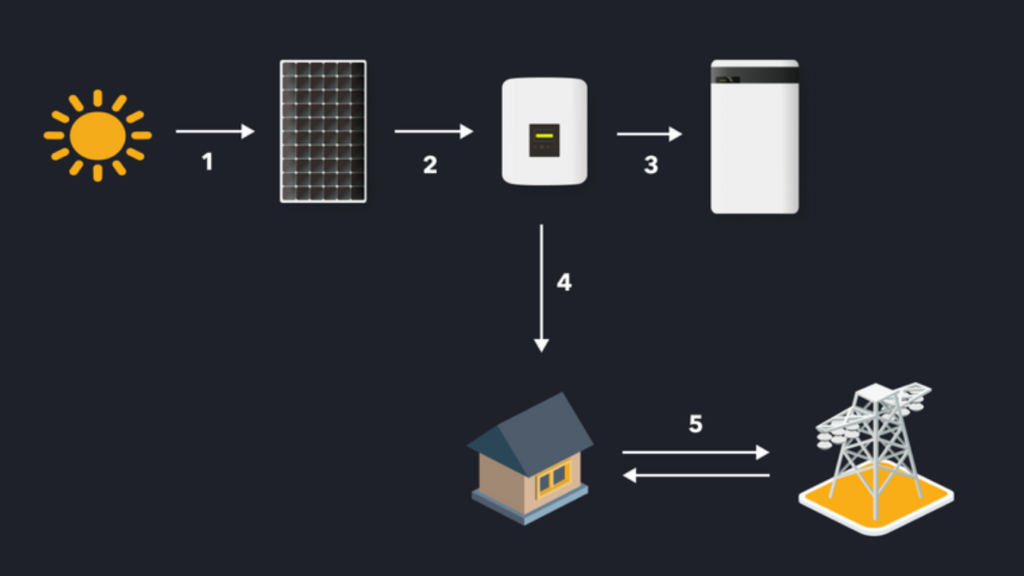
The operation of a photovoltaic cell is based on the ability of these semiconductor materials to capture light energy and then transform it directly into electric current. Photons from the sun strike the surface of the cell, transferring their energy to the electrons present in the material. This interaction allows the electrons to be freed and create an electric current.
Photovoltaic cells are at the heart of this incredible technology. They are primarily made of silicon, a plentiful material particularly efficient at converting sunlight. Each cell is an essential component of solar panels, which are then assembled to form large-scale photovoltaic power plants. You can learn more about the photovoltaic cell here.
The next-generation solar panels incorporate cutting-edge technologies to enhance energy production. They optimize energy yield and reduce the carbon footprint of installations. Innovations include the use of new materials and advanced manufacturing processes to maximize the efficiency and durability of solar panels.
However, the rise of solar power plants sometimes leads to challenges, such as electric grid congestion. This phenomenon slows the connection process of new projects to the national grid, illustrating the need to adapt infrastructures to the new demands of renewable energies.
Additionally, the integration of renewable energies in urban areas is generating increasing enthusiasm. Initiatives like the improvement of urban Microgrids help strengthen the resilience of cities in the face of future energy challenges and ensure a more equitable distribution of electricity.
Finally, the photovoltaic effect continues to inspire visionary projects. For example, Portland General Electric is investing in new projects to meet the growing demand for renewable energy. Meanwhile, South Australia has set the ambitious goal of becoming 100% renewable by 2027, highlighting the promising potential of solar technologies for a greener future.

The Photovoltaic Effect: Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the photovoltaic effect?
A: The photovoltaic effect is a physical phenomenon discovered in 1839 by Edmond Becquerel. It enables the production of electricity from sunlight, utilizing certain materials called semiconductors, which produce electricity when exposed to light.
Q: How does a photovoltaic cell work?
A: It directly converts the light energy from photons into electricity. This occurs through a semiconductor material, efficiently transforming light into electric current without destroying or consuming the materials in the process.
Q: What is the difference between the photovoltaic effect and the photoelectric effect?
A: While related, the photovoltaic effect specifically refers to the direct conversion of solar energy into electricity in solar cells, while the photoelectric effect is a more general term concerning the release of electrons from a material under light.
Q: What are the disadvantages of photovoltaic panels?
A: Some limitations include grid congestion due to prolonged connection delays. Additionally, their efficiency decreases when the weather is cloudy or at night, necessitating energy storage solutions for optimal performance.
Q: How does photovoltaics contribute to energy savings?
A: By converting sunlight into electricity, photovoltaic panels reduce dependency on non-renewable energies while lowering carbon emissions, making them a key solution for a sustainable energy transition.
Articles similaires
Thank you!
We will contact you soon.