History of Solar Energy
Solar energy has seen remarkable advancements over the past few decades. Harnessed since ancient times, it has experienced significant growth due to technological innovations and the awareness of the need to reduce carbon footprints.
As early as ancient times, civilizations were already using sunlight for various applications. The Greeks, for example, oriented their homes to benefit from better passive solar heating. During the medieval period, Persian scientists developed solar distillation techniques to produce drinking water in arid regions.
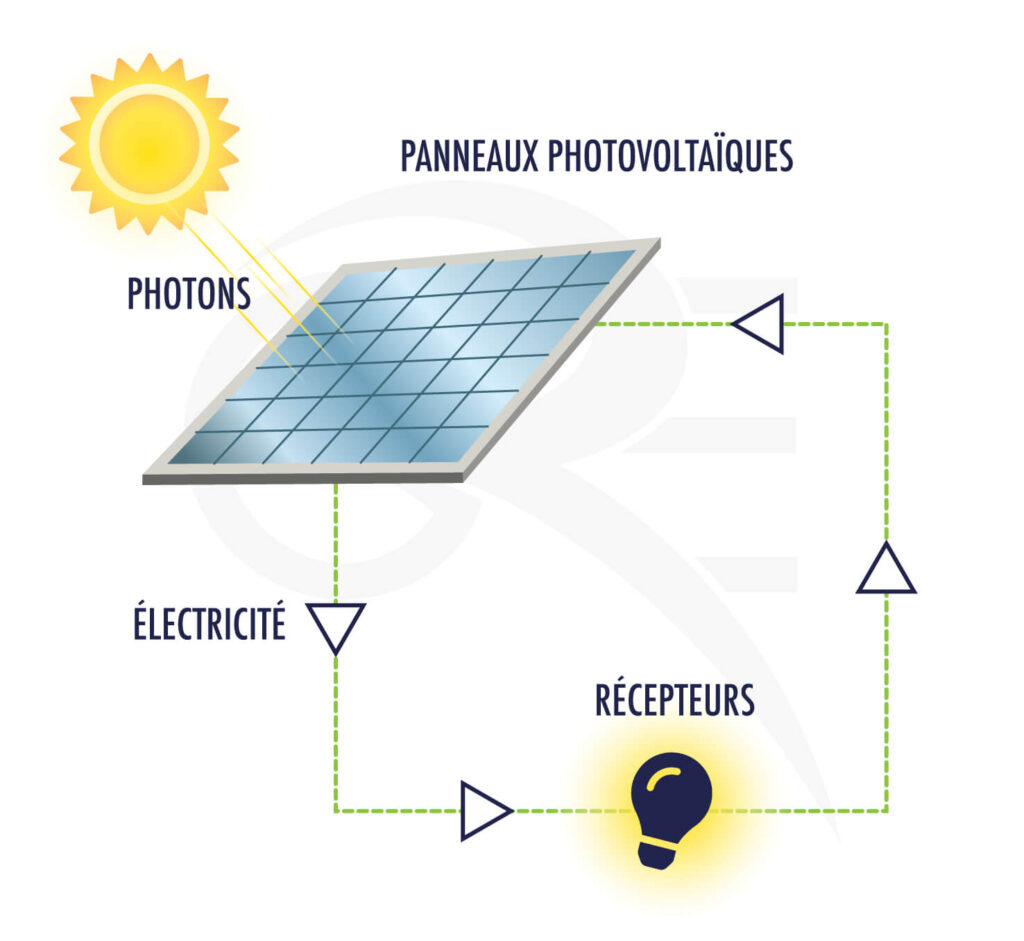
The 20th century marked a turning point in the industrialization of solar energy. The first photovoltaic cells emerged in the 1950s, enabling the direct conversion of light into electricity. It was during this time that the first solar panels were used to power satellites in orbit.
The 1970s represented a turning point with the oil crisis, which spurred interest in alternative energy sources. Many countries then invested in research and development of solar technologies, leading to significant improvements in efficiency and cost.
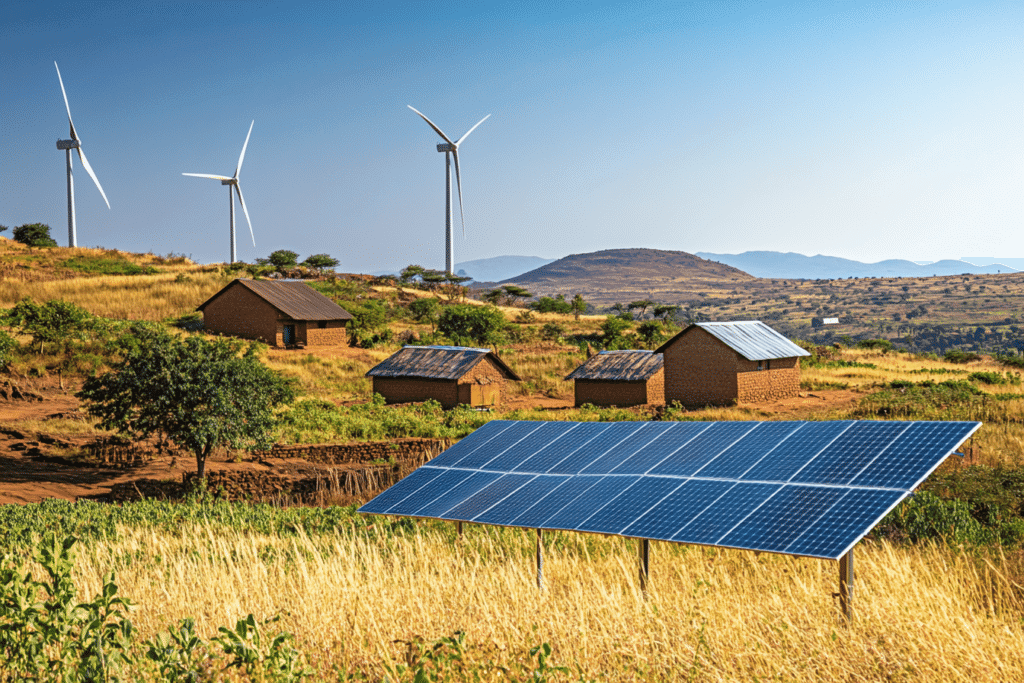
Today, thanks to technological breakthroughs and economies of scale, solar energy has become one of the most accessible and efficient renewable energy sources. Modern solar panels have much higher efficiencies and can be integrated into various applications, from solar farms to green buildings.
The future looks promising due to advancements in energy storage, allowing for more efficient use of the generated energy. The growing adoption of solar technologies significantly contributes to the global energy transition.
The Beginnings of Solar Energy
Solar energy has undergone remarkable evolution over the past several decades. The first uses of sunlight date back to ancient times when civilizations used mirrors to concentrate solar rays to start fires. However, it was in the 19th century that technological developments truly began to transform this energy source into a viable and innovative solution.
The year 1839 marks a key turning point with the discovery of the photovoltaic effect by Alexandre Edmond Becquerel. This discovery paved the way for the creation of the first photovoltaic cells, which convert sunlight into electricity. Throughout the 20th century, many scientists and engineers worked to improve the efficiency of these cells, making solar energy increasingly accessible.
It was in 1954 that Bell Laboratories produced the first silicon solar cell capable of efficiently converting sunlight into electrical energy. This moment is often considered the start of the modern solar energy era. From there, practical applications began to multiply, with pioneering projects such as powering spacecraft satellites.
In the 1970s, the oil crisis prompted many governments and companies to seek alternatives to fossil fuels. This led to a significant increase in investments in research and development in the solar field. Technological advancements allowed for cost reductions and improvements in solar panel efficiency, making this technology more competitive.
Today, solar energy is one of the most dynamic and promising energy sources. New technologies, such as bifacial solar panels or perovskite solar cells, continue to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Additionally, the development of energy storage solutions, such as high-capacity batteries, helps to compensate for the intermittency of solar production.
The future of solar energy is bright, supported by constant innovations and a growing awareness of the need to reduce carbon footprints. Many countries are now integrating solar energy into their energy transition strategies, aiming for ambitious renewable energy production goals. Solar technologies continue to develop, providing sustainable and accessible solutions for a clean energy future.
Current Technological Advancements
Solar energy has experienced significant evolution over the decades. The first uses of this energy date back to ancient times when civilizations used solar reflectors to ignite fires. The 19th century witnessed the discovery of the photovoltaic effect by Edmond Becquerel, a major advancement that laid the foundations for modern solar technology.
In recent decades, technological advancements in solar energy have been impressive. Innovative materials, such as monocrystalline silicon and polycrystalline silicon, have led to the development of more efficient and affordable solar panels. The establishment of solar tracking systems now allows panels to follow the sun’s path, thereby optimizing energy production.
Among the emerging technologies are:
- Perovskite solar cells, which promise increased efficiency and reduced production costs.
- Transparent solar panels, which can be integrated into building windows, maximizing the use of available space.
- Energy storage technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries and thermal storage solutions, which help mitigate the intermittency of solar production.
The integration of information and communication technologies (ICT) in solar systems also allows for smarter and more efficient management of the produced energy. Smart grids facilitate the distribution of electricity according to needs and availability.
The adoption of these technological innovations is not only beneficial from an environmental perspective, but it also represents a major economic opportunity. The transition to renewable energy sources, such as solar, significantly contributes to the reduction of the overall carbon footprint while creating new jobs and stimulating innovation.
Research and development initiatives continue to play a crucial role, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in solar production and efficiency. International collaborations and public and private funding are essential to accelerate this energy transition.
“`
Articles similaires
Thank you!
We will contact you soon.