When the Sun lights up our sky and the wind blows at full speed, nature offers a surplus of renewable energy. But there are times when this breeze dies down and clouds hide the light. To ensure that this energy dance is not interrupted, humanity must turn to innovative solutions. New techniques, ranging from reimagined batteries to compressed air systems to the kinetic energy of flywheels, promise to keep in reserve the energy we so desperately need during low periods. In this context, the challenges and opportunities related to the storage of renewable energy are more relevant than ever. For a future without interruptions and independence from fossil fuels, these technologies reflect an essential transformation of our energy grid.
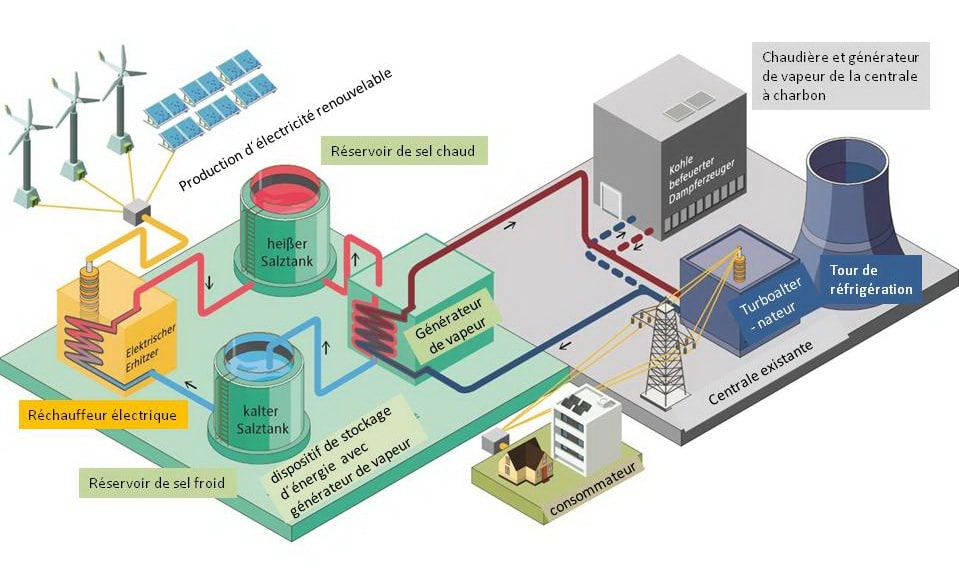
In a world where renewable energies like solar and wind are booming, the challenge of storing energy becomes crucial. As countries like Germany seek to reduce their dependence on fossil fuels, they encounter the dilemma of “Dunkelflauten,” periods when the sun and wind are absent. Lithium-ion batteries, while popular for short-term fluctuations, are not sufficient for prolonged periods. Engineers around the world are experimenting with innovative technologies to store energy, such as flywheels, compressed air, and alternative chemistry. Cost plays a crucial role in these developments, and new approaches like sodium-ion or hydrogen storage are being explored. The future of our energy transition will depend on our ability to define economical and sustainable solutions to retain this green energy beyond sunny days.

the urgency of mastering the intermittency of renewable energies
Renewable energies, despite their infinite potential, face a major challenge: their intermittent nature. When a day is sunny and the wind blows strongly, the energy produced can exceed demand and require a storage solution. Conversely, during periods of low sunlight or lack of wind, these energies are no longer sufficient to meet daily needs. This variability forces us to reconsider our energy model, which relies on constant availability via fossil fuels. The transition to a more sustainable system therefore depends on our ability to develop effective and accessible storage solutions.
exploring innovative storage solutions
To address this critical problem, several energy storage solutions are under examination. Among these, lithium-ion batteries represent the most widely used approach today, providing a response to the daily fluctuations of solar and wind energy. However, their cost and their dependence on limited resources, such as lithium, hinder their large-scale adoption for extended periods. To fill this gap, alternatives such as iron-air batteries and compressed air storage systems are being developed. These emerging technologies aim to provide sufficient storage capacity to cope with periods of low renewable energy production, also known as Dunkelflauten in Germany.
understanding the economic and environmental challenges
The cost of storage technologies plays a crucial role in either accelerating or slowing down the energy transition. Even though some solutions are beginning to compete with traditional options like lithium-ion batteries, large-scale implementation remains a challenge. Supporting policies, such as carbon taxes or incentives for technological collaborations could stimulate the market. Furthermore, the development of solutions must be carried out with a sustainable approach. Energy storage must not only be technologically viable but also minimize its ecological footprint to ensure a genuine advancement toward a sustainable energy future.
Articles similaires
Thank you!
We will contact you soon.