Imagine a future where every building contributes to the preservation of our planet. With geothermal energy, this goal becomes not only conceivable but accessible. By harnessing the Earth’s natural heat, we have an energy solution that deserves our full attention. Especially in the construction sector, this revolutionary method significantly reduces the carbon footprint of buildings, from heating to cooling.
Advanced geothermal systems offer an effective alternative to fossil fuels. With technologies such as geothermal heat pumps, heat can be transferred from the ground to our living spaces, drastically reducing our energy consumption. By integrating these infrastructures, not only do new constructions meet sustainability criteria, but this also applies to the rehabilitation of existing buildings. By prioritizing environmentally friendly materials and energy efficiency, the use of geothermal energy paves the way for sustainable development strategies, allowing us to build a greener future that respects our environment.

With rapid urbanization and growing concerns about climate change, the carbon footprint of buildings has become a major issue. Buildings are responsible for nearly 40% of global CO₂ emissions, making it crucial to adopt solutions that minimize this impact. Geothermal energy, often overlooked, emerges as a promising alternative to reduce this figure, offering both environmental and economic benefits.
The mechanisms of geothermal energy: understanding its potential
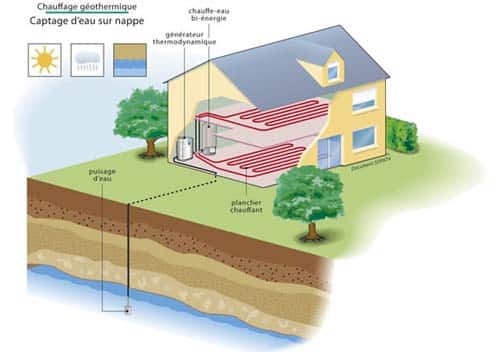
Geothermal energy works by harnessing the Earth’s natural heat for the heating and cooling of buildings. For example, geothermal heat pumps transfer heat from the ground to the interior, allowing for a comfortable temperature throughout the year. According to a report from Cerema, using a geothermal heat pump can reduce a building’s energy consumption by up to 75%. In other words, this technology enables the transformation of terrestrial heat into a key factor for energy savings.
Geothermal systems can be classified into two main categories: open-loop and closed-loop systems. Open-loop systems, which directly extract groundwater, are particularly efficient in regions with abundant water resources. In contrast, closed-loop systems use a heat transfer fluid, making them suitable for a wider variety of conditions. In the long run, these technologies not only reduce energy costs but also diminish carbon footprints, vital for sustainable construction initiatives.
Case studies and lessons from geothermal projects
Concrete examples can illustrate the effectiveness of geothermal energy. For instance, a renovation project of old buildings in a municipality in France integrated geothermal systems. The results showed a reduction in CO₂ emissions of over 50% compared to their pre-development levels. This project not only improved the carbon balance but also played a significant role in raising awareness among residents about the importance of sustainability.
Géothermie : chaud devant https://t.co/nnx8AuLW8F
— Les Echos (@LesEchos) April 24, 2024
In Sweden, an initiative in Stockholm demonstrated that an urban geothermal network could supply an entire neighborhood. Studies revealed that this approach could reduce their dependence on fossil fuels by 90%. Residents reported a significant reduction in their energy bills, which encourages other metropolises to consider similar solutions. Such initiatives show that it is possible to combine urban growth with environmental respect while creating a local dynamic favorable to innovation.
Strategies and recommendations for integrating geothermal energy into your projects
For building professionals and communities wishing to integrate geothermal energy, specific strategies are highly recommended. First, it is essential to conduct a thorough feasibility study of the geothermal resource, considering topography, geological conditions, and climate. This step is crucial to maximize the efficiency of the equipment.
Other recommendations include integrating energy management technologies into the building to monitor and optimize the performance of geothermal systems. Advanced control software can, for example, adapt the operation of heat pumps based on real-time demand, further improving the building’s carbon footprint.
Finally, it is crucial to educate stakeholders about the benefits of these systems. Organizing workshops and informational sessions can generate interest in geothermal energy and promote the large-scale adoption of this renewable energy. Moreover, funding geothermal projects, which generate an attractive return on investment, deserves the attention of investors. To discover how to optimize geothermal projects, the agency Celsius Energy provides tailored solutions, offering a pragmatic and innovative vision.
In summary, geothermal energy represents an essential lever to reduce the carbon footprint of buildings. By combining accurate data and realistic approaches, every stakeholder in the building sector can contribute to building a more sustainable energy future.

FAQ on geothermal solutions for reducing the carbon footprint of buildings
What is geothermal energy? Geothermal energy is a renewable energy source that harnesses heat from the ground to heat or cool buildings.
How does geothermal energy contribute to reducing the carbon footprint? By leveraging terrestrial heat, it significantly reduces CO2 emissions compared to traditional heating systems.
What types of geothermal systems are there? There are several systems, including geothermal heat pumps that circulate a fluid in buried loops to extract heat from the ground.
Can I install a geothermal system in an urban area? Yes, solutions offered by specialized companies allow for the integration of geothermal energy even in dense urban environments.
What are the economic benefits of geothermal energy? Although the initial investment may be high, savings on energy bills can quickly offset it, allowing for long-term profitability.
What environmental impacts are associated with geothermal installation? Geothermal projects generally have a much lower environmental footprint than fossil energy sources, thus contributing to environmental protection.
How can I estimate the return on investment of a geothermal system? You need to consider savings on energy bills, potential grants, and the increased property value resulting from this sustainable initiative.
Can geothermal energy work in all types of soil? Geothermal energy adapts to different soil types, but site-specific studies are often necessary to assess feasibility and efficiency.
What challenges are associated with installing a geothermal system? Challenges include the initial cost, the need for a soil study, and the installation of appropriate infrastructure, but these obstacles can be overcome with good planning.
Is geothermal energy safe? Yes, geothermal energy is considered a safe energy solution, as it uses natural resources sustainably without harmful side effects on human health.
Articles similaires
Thank you!
We will contact you soon.