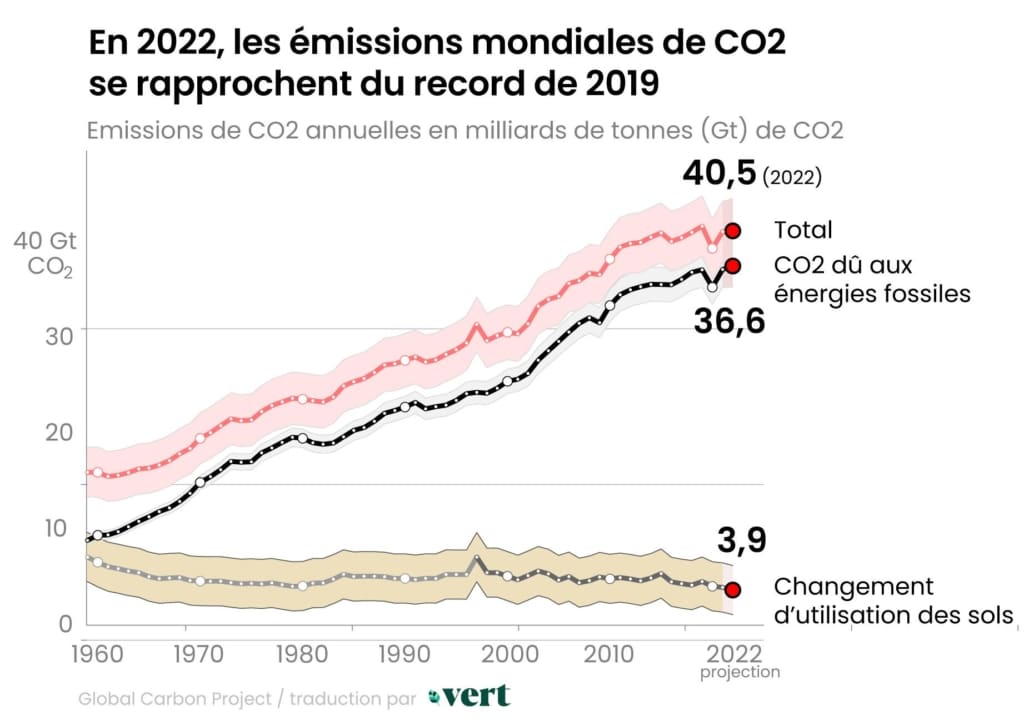
In 2024, global CO2 emissions from fossil fuels are reaching new heights, with an increase of 0.8% compared to the previous year, according to recent research conducted by the scientific team of the Global Carbon Project. Despite a decade of attempts to reduce these emissions, the continued growth of coal, oil, and gas poses a major challenge in the fight against climate change. The data indicates no downward trend in global emissions, while climate events like the El Niño phenomenon contribute to worsening this already heavy burden.
In 2024, global CO2 emissions from fossil fuels have reached a historic level, marking an increase of 0.8% compared to the previous year, with total CO2 emissions, including those from land-use changes, estimated to reach 41.6 billion tons this year. These emissions have continued to rise despite the urgency of reducing them to mitigate climate change.
Emissions from deforestation and wildfires have also increased due to drought conditions exacerbated by the El Niño climate phenomenon. Atmospheric CO2 levels continue to soar, fueling an increasingly dangerous global warming. Emissions from fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas contribute to this increase, representing 41%, 32%, and 21% of global fossil emissions, respectively.
The impact of climate warming is intensifying, and rapid and deep actions are needed to reduce these emissions and hope to meet the goals set by the Paris Agreement. Progress is noted with the increase of renewable energies and electric cars, as well as the decrease in deforestation observed over the past decades.

record rise in CO2 emissions in 2024
In 2024, global CO2 emissions will reach a historic level with a projected increase of 0.8% compared to the previous year, reaching 41.6 billion tons. This concerning rise is partly due to an uptick in oil, gas, and coal emissions. This situation highlights the importance of fossil fuels in the current climate warming. Experts agree that despite some progress in renewable energies, there is still no sign of a peak in fossil CO2 emissions. To learn more, consult this comprehensive study: BFMTV.
impacts of fossil fuels and reduction efforts
As the world seeks to mitigate the devastating effects of climate change, CO2 emissions from fossil fuels remain a critical issue. Traditionally, the industrial and energy sectors are at the forefront of emissions reduction, but with current figures, the outlook remains uncertain. For more details, visit this link: Techniques de l’Ingénieur. While some countries succeed in reducing fossil consumption in favor of renewable energies, others continue to increase their use. These differences, at the global level, add additional challenges in the fight against global emissions.
perspectives and solutions to combat the increase in emissions
By analyzing current trends, the need for effective solutions to tackle the increase in CO2 emissions is undeniable. Projections suggest rapid and drastic interventions are necessary to keep the rise in global temperature below 1.5°C. Although many initiatives are underway, such as the growing investment in hydrogen, uncertainty remains regarding their future impact. Check this link for more details on the potential of hydrogen: Green Just Now. The absorption of CO2 by forests and oceans remains crucial, but it is continually compromised by climate challenges. More than ever, each country must accelerate its efforts to reduce its carbon footprint, adopting a trajectory towards net zero.
Articles similaires
Thank you!
We will contact you soon.