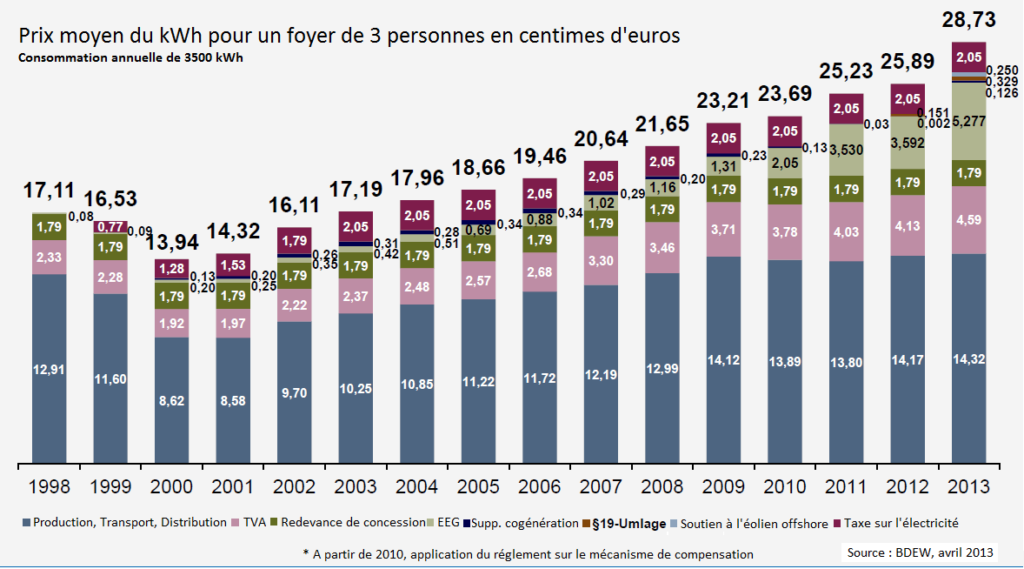
Germany is undergoing a major reorganization of cost distribution to promote the integration of more renewable energy into its electricity grid. With the ambition of covering at least 80% of its electricity consumption with renewable energy by 2030, this profound transformation requires significant adaptation of its energy infrastructure. To achieve this, various measures have been adopted, including the reform of the Renewable Energy Sources Act in 2021. Reaching this ambitious goal involves the essential modernization of electricity grids and better integration of renewable energy into the market, making this energy transition crucial both for Germany and for the global energy future.

Germany has undertaken a significant reorganization of cost sharing to promote the integration of renewable energies into its electricity grid. This initiative, marked by ambitious legislation and the essential modernization of infrastructures, aims to ensure that by 2030, at least 80% of the country’s electricity consumption comes from renewable sources. Reforms such as the Renewable Energy Sources Act of 2021 (EEG 2021) and various market support measures aid this transition.
The Energy Transition, a Generational Project
The energy transition in Germany, also known as Energiewende, is an ambitious project aimed at profoundly transforming the country’s energy landscape. By 2030, the German government wants 80% of electricity consumption to come from renewable sources. To achieve this, Germany has implemented a series of reforms and legislative measures to restructure its energy mix and reduce its dependence on fossil fuels and nuclear energy.
The Reform of the Renewable Energy Sources Act of 2021 (EEG 2021)
Last July, the Bundestag adopted the reform of the Renewable Energy Sources Act, a key step in accelerating the energy transition. Starting January 1, 2021, this new legislation provides for a redistribution of the costs associated with the production and integration of renewable energies. This law aims in particular to encourage investments in green technologies while ensuring a better distribution of financial burdens among producers, consumers, and the state.
The Essential Modernization of Electricity Grids
To achieve its ambitious goals, Germany must modernize its electricity grids. This modernization is essential to accommodate a growing volume of electricity produced from renewable sources. By 2030, Germany expects that 30% of gross final energy consumption will come from renewable energies, which requires robust and flexible infrastructures. Implementing this modernization involves significant investments in the electricity distribution and transmission network.
Market Integration and Direct Sales
Successful integration of renewable energies into the electricity market involves direct sales. This mechanism allows renewable energy producers to sell their electricity directly on the market, thus benefiting from better compensation while contributing to the stability of the grid. However, this support is conditioned by performance and quality obligations to ensure the stability and reliability of the electricity network.
Support Measures for the Transition
Germany has implemented several measures to support the transition towards a more sustainable energy mix. In addition to the reform of the Renewable Energy Sources Act, other initiatives aim to encourage investments in green infrastructures, subsidize clean energy technologies, and promote research and development in the sector. These measures are crucial for reducing dependence on fossil fuels and ensuring a stable and sustainable energy supply.
In conclusion, the reorganization of cost sharing for the integration of renewable energies in Germany is an essential step in the country’s energy transition. Through ambitious legislative reforms, essential infrastructure modernization, and various support measures, Germany positions itself as a global leader in promoting green energies.
[#EnR] Ce que l'#éolien rapporte à la France : 3️⃣ chiffres pour mieux comprendre la contribution de cette énergie #renouvelable aux finances publiques et à notre indépendance énergétique ?
— France renouvelables (@f_renouvelables) June 27, 2024
9️⃣ milliards € : c'est ce que l'éolien aura rapporté à l'État français entre 2022 et… pic.twitter.com/Mf9BkaCVDh
Articles similaires
Thank you!
We will contact you soon.