Use of Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is a sustainable energy source that uses heat from the depths of the Earth. This heat is generated by the natural decay of radioactive elements in the Earth’s core and can be captured and converted into electricity or used to heat buildings. Geothermal energy represents a clean and renewable alternative to fossil fuels.
The process of capturing geothermal energy involves drilling deep wells to access hot water or steam reservoirs located beneath the Earth’s surface. This water or steam is then used to power turbines that generate electricity. Geothermal facilities can operate continuously, providing a stable energy production compared to intermittent sources like wind or solar.
One of the main advantages of geothermal energy is its low carbon footprint. Compared to fossil fuel power plants, the greenhouse gas emissions from geothermal facilities are negligible. Additionally, geothermal energy requires little land and does not impact air quality.
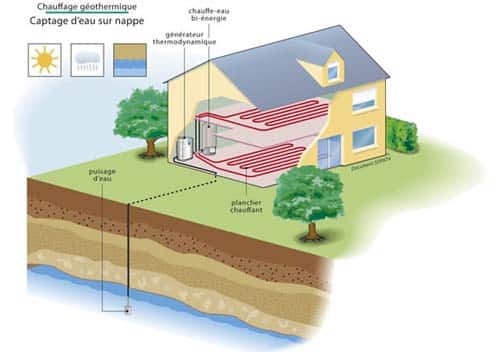
In addition to electricity production, geothermal energy can be used to power heating and cooling systems. These geothermal systems in residential and commercial buildings extract heat from the ground in winter and discharge it back to the ground in summer, thus functioning as very efficient heat pumps.
Technological innovations in the geothermal field are constantly improving the efficiency of facilities. Horizontal drilling, binary fluid systems, and the use of smart sensors are all advances that help make this energy even more attractive and accessible.
For those looking to invest more in geothermal projects, it is essential to consider several factors:
- The availability of local geothermal resources
- The initial installation costs
- Regulations and government incentives
- Potential environmental impacts
Geothermal energy offers immense potential to support the energy transition and promote a cleaner and more sustainable future. With the right technologies and appropriate support, it can play a key role in diversifying the energy mix and reducing carbon emissions globally.
Well Drilling
Geothermal energy is a sustainable and clean source that uses heat from the Earth’s core. This heat can be converted into electricity or used directly for heating. Harnessing geothermal energy helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and provides a stable and continuous energy source.
The use of this energy is varied. Geothermal systems can be used to generate electricity in geothermal power plants, where hot water or steam from deep within the Earth turns turbines. Other systems, like geothermal heat pumps, can be installed in buildings to provide heating and cooling efficiently and cost-effectively.
To harness this energy, well drilling is typically necessary. This process involves digging wells into the ground to reach hot water or steam reservoirs located at various depths. The drilling can vary in depth, ranging from a few hundred meters to several kilometers, depending on the local geology and energy needs. The main steps include:
- Preliminary geological study to identify potential sites
- Environmental assessment and obtaining necessary permits
- Drilling the well with specialized equipment
- Installing the pump to extract hot water or steam
The management of drilling and operation requires considerable technical expertise to ensure the safety and efficiency of the facility. Continuous monitoring is also essential to maximize the lifespan of the well and optimize heat extraction.
Electricity Production
Geothermal energy, a renewable energy resource, uses heat stored in the Earth’s subsurface. This clean energy meets various energy needs, such as heating, cooling, and electricity generation.
Its use is an effective way to reduce carbon footprint and lessen our dependence on fossil fuels. With adequate facilities, it is possible to harness the heat found in the deep layers of the Earth’s crust, sometimes extending several kilometers deep. Geothermal energy is not only sustainable but also stable, providing continuous energy production unlike solar and wind energies, which depend on weather conditions.
The main uses of geothermal energy include:
- Heating and cooling buildings using geothermal heat pumps.
- Electricity production in geothermal power plants.
- Industrial applications requiring constant and high heat.
For electricity production, geothermal energy is captured by wells drilled into the ground. The steam or hot water obtained is used in a geothermal power plant to turn a turbine connected to a generator, thereby producing electricity. This process allows for constant and reliable electricity generation, with no greenhouse gas emissions.
There are several techniques to exploit this energy:
- Dry steam plants, using steam directly from geothermal reservoirs.
- Binary cycle plants, employing a secondary fluid to extract heat.
- Flash steam plants, which separate steam from hot water to drive turbines.
With its multiple advantages and development potential, geothermal energy represents a promising solution for a greener energy future, meeting energy needs while preserving the environment.
Articles similaires
Thank you!
We will contact you soon.