Deep geothermal energy opens up to us as a fascinating renewable energy source, harnessing the incredible heat from the Earth’s mantle. In the Île-de-France region, for example, these valuable resources are found at depths between 600 and 1,000 meters, where temperatures range from 25 to 40°C. Thanks to an ingenious drilling system, water from deep aquifers is used to supply heating networks or even produce electricity. This is a true opportunity to revolutionize our energy approach, combining efficiency and respect for the environment.
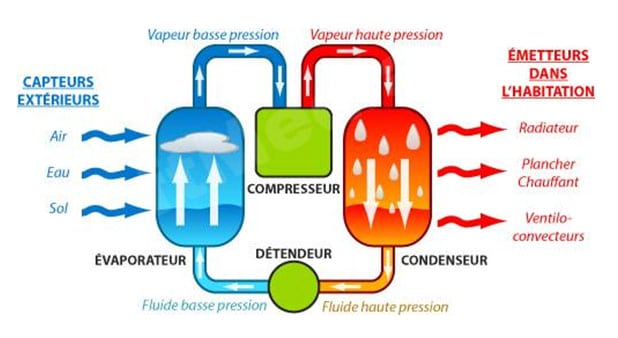
Deep geothermal energy is a renewable energy source that harnesses the intense heat from the Earth’s mantle. This heat is captured by drilling at great depths, generally over 200 meters, to produce heat, steam, or even electricity. Unlike surface geothermal energy, which relies on shallower resources, deep geothermal energy is capable of providing much higher temperatures and energies.
In the Île-de-France region, for example, deep geothermal resources are located between 600 and 1,000 meters deep, with temperatures ranging between 25 and 40°C. These temperatures allow for the transfer of heat to heating networks for building heating. This technology is implemented in many regions around the world, with notable examples such as Alsace in France, which has significant geothermal potential.
One of the great advantages of deep geothermal energy is its ability to provide renewable energy locally and sustainably. Given that this energy source is virtually inexhaustible and does not depend on climatic conditions, it offers a reliable and eco-friendly energy solution. This translates into a significant reduction in the carbon footprint of buildings and infrastructures that exploit it. To learn more about how to reduce the carbon footprint of buildings, click here.
The drilling technology used to exploit geothermal energy is very similar to that used in the oil industry, which allows these methods to be transformed into a carbon-free energy source. Once the initial drilling is completed, geothermal energy can be exploited continuously with little maintenance, making it an economically viable long-term option. The technology is mature enough that it is expanding, notably in countries like China, which is launching the construction of geothermal power plants in Africa to support the energy transition. Learn more about this development here.
Technologically, deep geothermal energy uses geothermal pumps to extract buried heat. These systems also efficiently manage cold, which means that in certain industrial applications, the same system can provide both heating and cooling. Recent technological advances, such as the pilot electrolysis project at the Bluescope plant, demonstrate the effectiveness and sustainability of these systems. For more information, visit this resource here.
In terms of evolution, geothermal energy is a historical know-how used for millennia in some countries for cooking and heating. However, its potential is not limited to its initial capacity. Today, it plays a key role in the diversification of the global energy mix and offers the opportunity to accelerate the transition to a greener and more sustainable future. To explore new energy strategies for the future, follow this practical guide here.

FAQ on Deep Geothermal Energy
Q: What is deep geothermal energy?
A: Deep geothermal energy is a renewable energy source that harnesses the intense heat from the Earth’s mantle. Unlike surface geothermal energy, it can produce, in addition to heat and/or cold, electricity through drilling that goes well beyond 200 meters in depth.
Q: Where are deep geothermal resources found in the Île-de-France region?
A: In the Île-de-France region, deep geothermal resources are generally located between 600 and 1,000 meters deep, where temperatures range from 25 to 40°C.
Q: How does deep geothermal energy work?
A: Deep geothermal energy works by capturing, through drilling, water from deep aquifers and then transferring it to heating networks for heating and potentially for electricity production.
Q: What are the advantages of deep geothermal energy?
A: Deep geothermal energy has the advantage of providing local and sustainable energy, with a reduced carbon footprint. It is particularly well-suited to power buildings while minimizing environmental impact.
Q: What is the difference between surface and deep geothermal energy?
A: Surface geothermal energy uses resources located a few hundred meters deep mainly for heating, while deep geothermal energy draws from greater depths to produce heat and electricity.
Articles similaires
Thank you!
We will contact you soon.