Bioremediation is an innovative and natural method that uses living organisms to decontaminate polluted soils and waters. This technique offers a sustainable solution against pollutants such as hydrocarbons, heavy metals, and other chemicals. In this article, we will explore how bioremediation works, the different types of bioremediation, and the benefits it brings to the environment.
What is bioremediation?
Bioremediation relies on the use of living organisms such as bacteria, fungi, and plants to eliminate or neutralize contaminants present in the environment. These organisms have specific properties that enable them to degrade or transform pollutants into less harmful or harmless products.
The different types of bioremediation
There are several bioremediation techniques, each suited to a particular type of pollution:
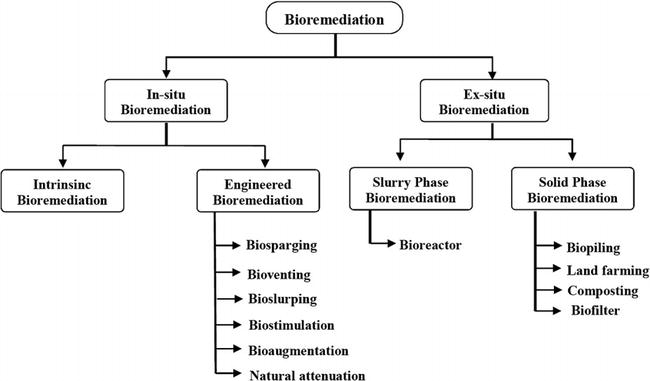
- In situ bioremediation: This method is applied directly at the contaminated site. Organisms are introduced into the polluted soil or water and begin to work on-site to degrade the contaminants.
- Ex situ bioremediation: In this case, the polluted soil or water is extracted from the site and treated elsewhere. This can include processes such as biocomposting or treatment in biological reactors.
- Phytoremediation: Use of plants to absorb, accumulate, and degrade pollutants. Plants suitable for phytoremediation have the ability to extract heavy metals and other toxic substances from the soil.
The benefits of bioremediation
Environmental solution
Bioremediation is an ecological solution that minimizes the use of aggressive chemicals and avoids destructive decontamination methods. This approach helps preserve soil structure and biodiversity while effectively eliminating contaminants.
Sustainability and cost
Compared to traditional methods, bioremediation is often more cost-effective and sustainable. It utilizes natural and renewable resources to treat pollutants, thereby reducing material and energy costs. Additionally, it can be implemented across a wide range of contaminated sites, making it a flexible and adaptable method.
Applications of bioremediation
Soil decontamination
Scientists have conducted experiments by disseminating plants and fungi to remove heavy metals from contaminated soils. For example, certain plants like sunflower and poplar are particularly effective for heavy metal extraction, while some fungi can break down complex hydrocarbons.
Treatment of polluted waters
Bioremediation can also be used to treat polluted waters. Specific microorganisms are introduced to degrade contaminants in surface or groundwater, thus providing a natural and effective method to purify rivers and aquifers.
The challenges of bioremediation
Despite its many advantages, bioremediation presents certain challenges. The success of this method depends on various factors, including the nature and concentration of pollutants, environmental conditions, and the availability of appropriate organisms. A deep understanding of the interactions between organisms and pollutants is essential to optimize bioremediation processes.
In summary, bioremediation offers a promising and environmentally friendly approach to the decontamination of soils and waters. Through the intelligent use of living organisms, it is possible to restore natural ecosystems while reducing our ecological footprint. With ongoing research and technological developments, this method could play a key role in the fight against pollution on a global scale.
Articles similaires
Thank you!
We will contact you soon.