The evaluation of the sustainability of agricultural inputs is a crucial topic in the context of the transition to more environmentally friendly agriculture. Indeed, the quality and impact of products used in agriculture play an essential role in the preservation of natural resources and the reduction of the ecological footprint of this activity. It is therefore vital to measure and analyze the sustainability of agricultural inputs to promote sustainable agricultural practices that respect the planet.
Importance of Agricultural Inputs

The importance of agricultural inputs in our society cannot be underestimated. With a global population of nearly 8 billion people, agriculture plays a crucial role not only in food supply but also in the employment of 26% of the global workforce. However, there is a misconception that all inputs, such as fertilizers, seeds, and crop protection products, are harmful to the environment.
Agricultural Technologies and the Environment
Contrary to this perception, agricultural technologies have allowed for feeding a growing population over the past six decades without significantly increasing cultivated land. These technologies act as powerful levers to reduce the impact of agriculture on the environment, for example by decreasing the carbon footprint and reducing water consumption.
Innovation and Sustainability
Specific treatments for seeds and soils, as well as modern spraying techniques, reduce farmers’ dependence on resource-intensive activities such as irrigation and fertilization. On the other hand, some innovations facilitate the practice of regenerative agriculture, thereby improving soil health, reducing erosion, and promoting biodiversity.

Reducing Deforestation
Every product, practice, or service that maximizes the productivity of existing agricultural land decreases the likelihood that farmers will need to clear forests or other vegetation. With a projected global population of 10 billion by 2050, increasing food production is imperative.
Transparency and Accountability
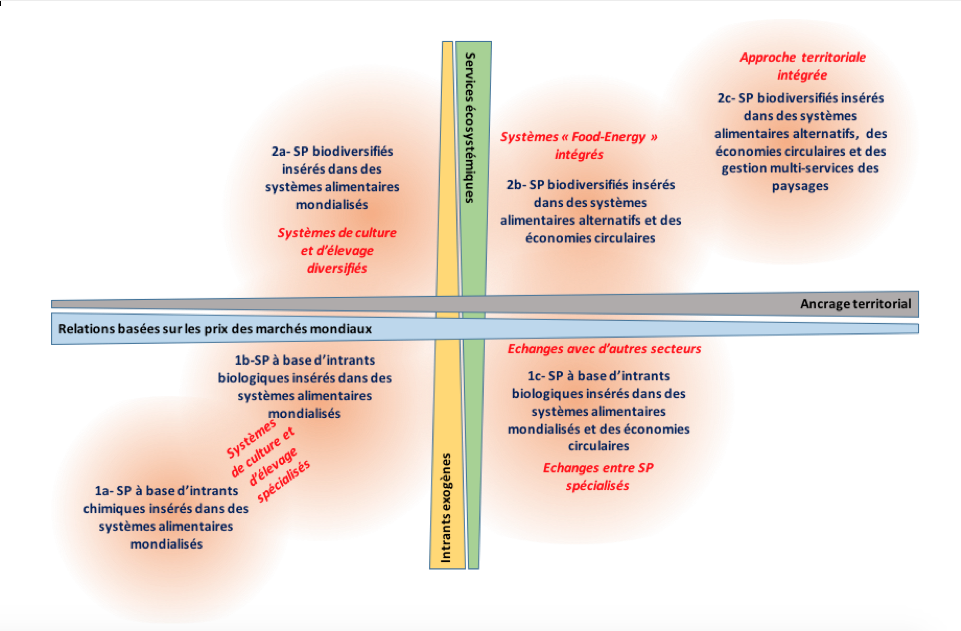
The Syngenta Group has developed an innovative tool called the Portfolio Sustainability Framework (PSF) to measure how its products help farmers achieve better yields with less environmental impact, while also assessing the sustainability of its own operations. This tool is based on the idea that what is measured can be better managed and improved.
PSF Methodology
The PSF systematically maps the entire product portfolio of Syngenta according to two key dimensions: sustainable benefits and alignment with stakeholders. The products are classified into three tiers based on their environmental benefits and their alignment with stakeholder expectations.
Collaboration and Learning
Dans l'industrie, la durabilité et le respect de l'environnement sont des impératifs !?
— La French Fab (@LaFrenchFab) June 8, 2024
Rejoignez-nous à l'Eco Class Factory de Strasbourg, le 13 juin, pour repenser ensemble nos processus de production et rester à la pointe de l'innovation ? https://t.co/QgoYcixgCW#FrenchFab pic.twitter.com/rh3a1arwq2
To develop the PSF, Syngenta collaborated with various stakeholders, including ESG rating agencies, financial analysts, banks, and NGOs like The Nature Conservancy. The company has also learned from existing tools and frameworks in the agricultural industry.
Syngenta’s commitment to this mission is all the more crucial as the future of sustainable agriculture depends on such methodological innovations to systematically assess and improve the sustainability of agricultural inputs.
List of Relevant Axes
- Axis 1: Importance of Agricultural Inputs
- Time: Global food supply, employment
- Axis 2: Technologies and Environment
- Impact: Reduction of carbon footprint, water consumption
- Axis 3: Innovation and Sustainability
- Resources: Regenerative agriculture, biodiversity
- Axis 4: Reducing Deforestation
- Objective: Maximization of agricultural land
- Axis 5: Transparency and Accountability
- Tool: Portfolio Sustainability Framework (PSF)
- Axis 6: PSF Methodology
- Evaluation: Sustainable benefits, stakeholders
- Axis 7: Collaboration and Learning
- Collaboration: NGOs, ESG agencies
Articles similaires
Thank you!
We will contact you soon.