The relentless quest to improve renewable energy storage is making significant progress with the introduction of a new electrolyte. By combining potassium, sodium, and sulfur, this technology promises not only a long-term storage solution but also increased efficiency. By optimizing the performance of electrode materials, this new development could revolutionize our approach to energy storage. Innovations such as solid-state batteries and flow batteries are redefining what we thought was possible, paving the way for more sustainable and optimal exploitation of renewable energy resources.

Technological advancements in the field of renewable energy storage are in full swing. A new type of electrolyte, combining potassium, sodium, and sulfur, opens new perspectives for more effective long-term storage. This article explores recent innovations, next-generation electrode materials, and potential technologies that will revolutionize the energy sector.
A revolutionary combination of materials
The major challenge of renewable energy storage lies in the ability to store this energy efficiently and sustainably. A new type of electrode material, incorporating potassium, sodium, and sulfur, has proven particularly promising. This combination allows for more efficient storage and use of energy while reducing production costs and initial investments.
Advantages of a new electrolyte
This new electrolyte significantly enhances battery performance by offering better energy density. This technological advancement not only increases storage capacity but also extends battery life. By optimizing charging and discharging cycles, it also minimizes energy losses and maximizes the use of renewable resources.
The Li-S battery technology
Saft, a leading company in the battery industry, has prioritized lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery technology with a solid-state electrolyte. These batteries offer energy density that is significantly superior to traditional batteries, which is crucial for applications such as next-generation electric vehicles and large-scale energy storage systems.
Redox Flow Batteries
The HIGREEW project, which began in November 2019, focuses on advancing Redox Flow batteries. These batteries use two tanks to store reactants and an ionic conductive membrane to manage the flow of electrons. Their flexibility and ability to provide large-scale storage solutions make them particularly suitable for renewable energies such as wind and solar.
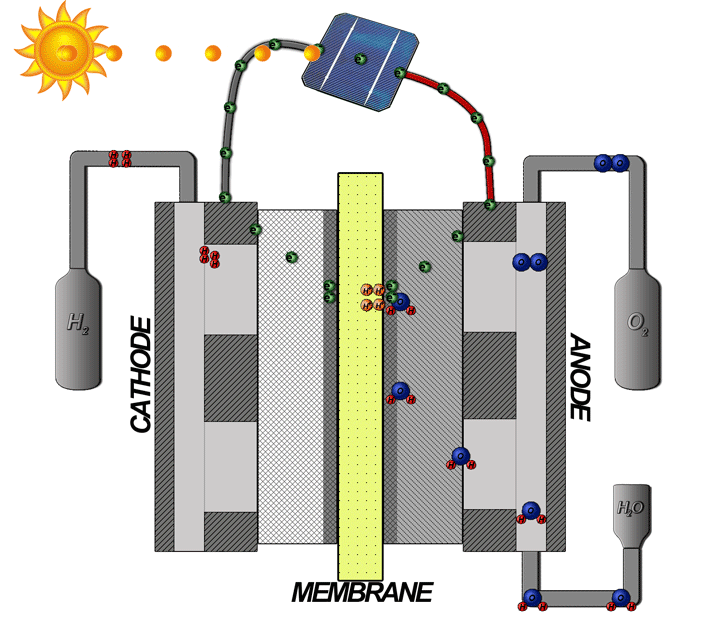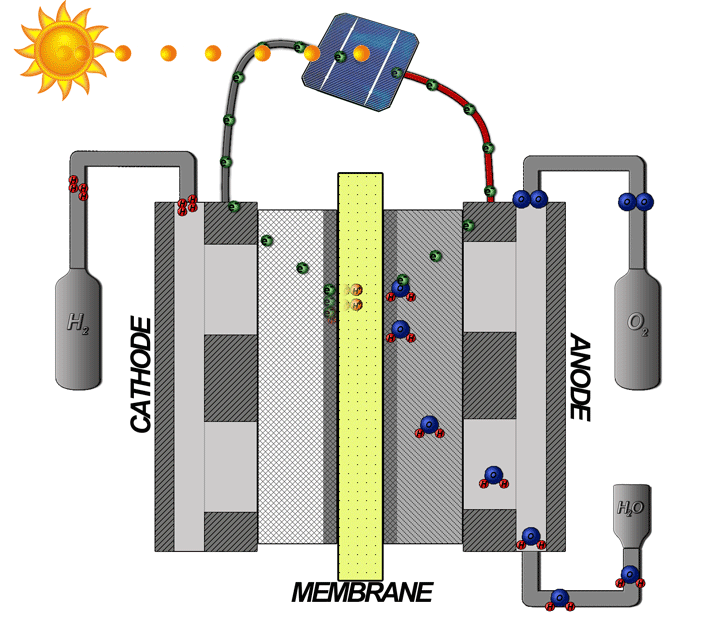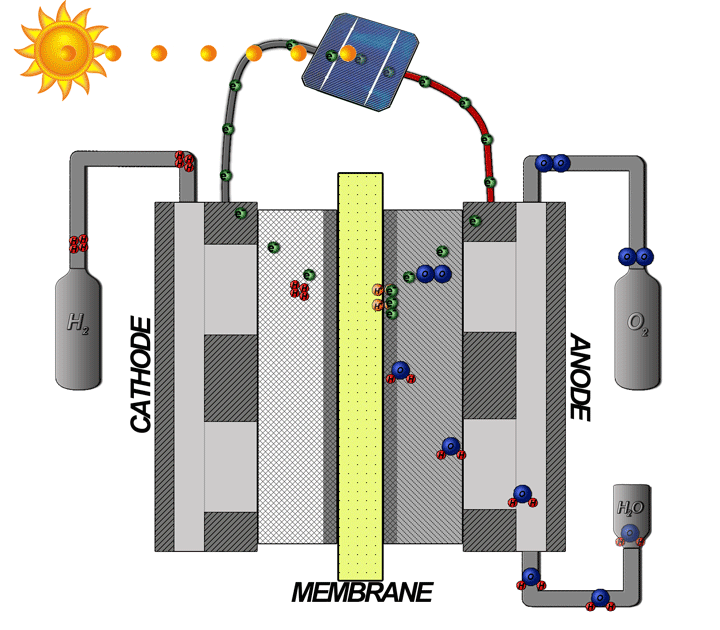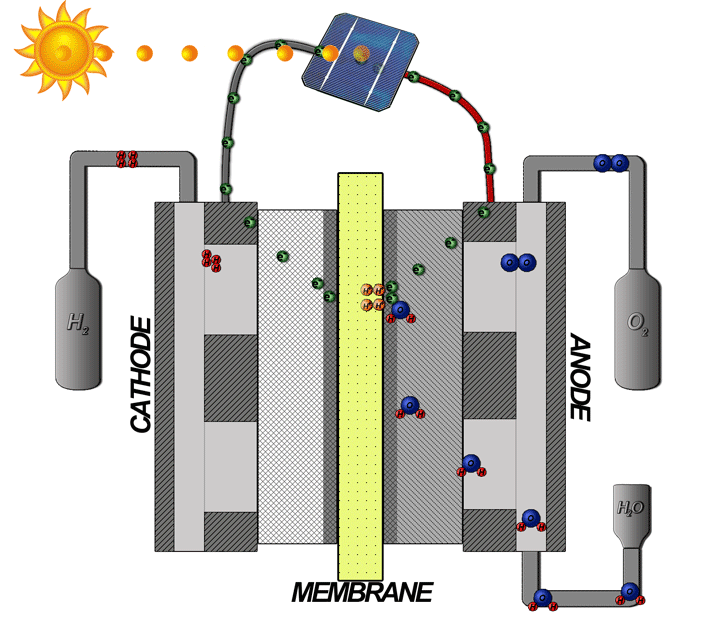
Hydrogen Fuel Cells
The hydrogen fuel cell, often mentioned as the most promising fuel cell, converts electricity stored in hydrogen into electrical energy. This technology represents a viable solution to meet future energy needs while minimizing environmental impact.
The future of energy storage technologies
Research projects focused on rhubarb-based batteries and new materials for solid batteries show that innovation is at the forefront of concerns. Synthesizing thousands of molecules to create more efficient and durable electrolytes has become a priority for developing revolutionary energy storage solutions.
Batteries solides : un nouvel électrolyte prometteur identifié grâce à l'IA https://t.co/T0u6bA7O1s pic.twitter.com/w4xqemuC0V
— Le Journal du Geek (@JournalDuGeek) January 11, 2024
Articles similaires
Thank you!
We will contact you soon.